Background
In Silverlight 4, Out Of Browser with elevated permission is significantly improved, now the OOB application has more privilege in accessing system resources such as the ability of accessing Isolated Storage, manipulating COM objects, access local registry entries, or even invoke Microsoft Speech API to phonate.
Essentially, to achieve this, the main improvements are:
- Microsoft gives Silverlight 4 OOB applications ability to request elevated trust.
From Trusted Applications
You can configure out-of-browser applications to require elevated trust. After installation, these trusted applications can bypass some of the restrictions of the security sandbox. For example, trusted applications can access user files and use full-screen mode without keyboard restrictions.
- A new concept coming from .NET 4.0 called “late binding”, the C# key word: dynamic could be use to declare a undetermined type at build time, during runtime, Microsoft.CSharp.RuntimeBinder will do dynamically building.
Introduction
My post is going to concentrated discuss about elevated trust, so read the articles below if you have any issues about creating OOB and request elevated permission.
How to: Configure an Application for Out-of-Browser Support
How to Configure your Silverlight App to run in Elevated Trust Mode
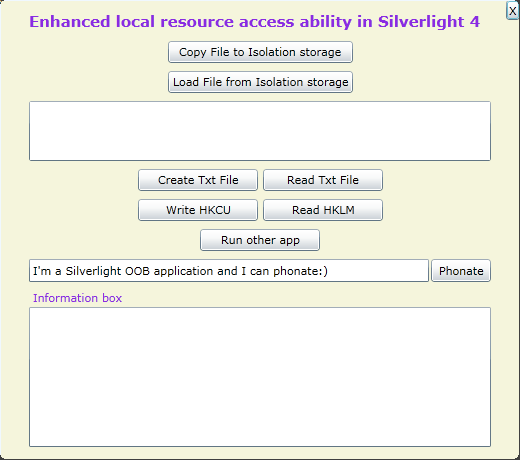
I developed a simple Silverlight OOB demo, it will access local system resources including:
- Let user choose some file(s) and then copy them to isolated storage.
- Access isolated storage enumerate all files.
- Create a txt file under drive C: by invoking “Scripting.FileSystemObejct”, as well as read its content back.
- Write registry entry under HKEY_CURRENT_USER, read registry entry under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, by using “WScript.Shell”.
Note: Silverlight OOB application will NOT have write permission to HKLM, it only have read permission.
- Run another executable files located on the system by using “WScript.Shell”.
- Phonate a sentence user input into the textbox.
Screenshot
After installing on the system, its UI is shown below (I know it is really poor… Sorry ):
):
Implementation
The elevated permission ONLY enabled in Out Of Brower scenario, so in our Silverlight application we need check whether currently it is running out of browser:
if(Application.Current.IsRunningOutOfBrowser)
// Access local file, registry, COM, etc.
In additional, to invoke COM objects, we need check whether AutomationFactory is available:
if (AutomationFactory.IsAvailable)
OK here we go to see the code behind to implement elevated permission.
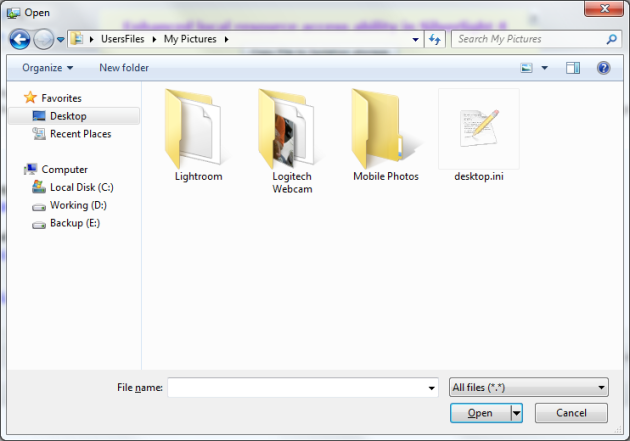
1. Clicks on Button – “Copy File to Isolated Storage acces”, a File open dialog will popup, screenshot below:
Code behind to open file dialog:
OpenFileDialog dlg = new OpenFileDialog { Filter = "All files (*.*)|*.*", Multiselect = true };
var dlgResult = dlg.ShowDialog();
Read selected file(s) and copy them to isolated storage:
IsolatedStorageFile iso = IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForApplication();
foreach (FileInfo file in dlg.Files)
{
using (Stream fileStream = file.OpenRead())
{
using (IsolatedStorageFileStream isoStream =
new IsolatedStorageFileStream(file.Name, FileMode.Create, iso))
{
// Read and write the data block by block until finish
while (true)
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[100001];
int count = fileStream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
if (count > 0)
{
isoStream.Write(buffer, 0, count);
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
}
}
Code behind for “Load file from isolated storage”:
var isoFiles = from files in IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForApplication().GetFileNames()
select files;
2. Create a text file at “C:\WayneTestSL4Fso\WayneTest.txt”, please note: if you use System.IO.File to do such operation you won’t success, I guess it is because elevated trust is still not directly implemented in a lot of managed assemblies. Here in my demo I used Scripting.FileSystemObejct:
private String folderPath = "C:\\WayneTestSL4FSO";
private String filePath = "C:\\WayneTestSL4Fso\\WayneTest.txt";
using (dynamic fso = AutomationFactory.CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject"))
{
if (!fso.FolderExists(folderPath)) fso.CreateFolder(folderPath);
dynamic txtFile = fso.CreateTextFile(filePath);
txtFile.WriteLine("Some text...");
txtFile.close();
}
P.S. While I first time used “dynamic” keyword within a using statement, I was a little bit surprised, I can simply try to dispose a dynamic object without checking whether it has implemented IDisposible, hence I tried run using (dynamic x = 8 ), then I got this :
:
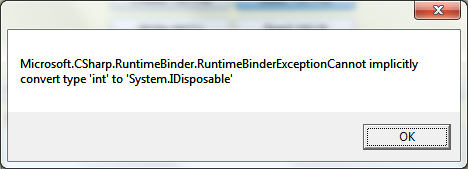
OK, let’s back to the code implementation for reading the text file I just created,
var fileContent = String.Empty;
using (dynamic fso = AutomationFactory.CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject"))
{
dynamic file = fso.OpenTextFile(filePath);
fileContent = file.ReadAll();
file.Close();
}
3. Registry write/read, please note: we can only have registry write permission to HKCU NOT HKLM, we have read permission to HKLM entries.
using (dynamic wScript = AutomationFactory.CreateObject("WScript.Shell"))
{
// Only has write permissin to HKCU
wScript.RegWrite(@"HKCU\Software\WayneTestRegValue",
"SomeStrValue", "REG_SZ");
}
using (dynamic wScript = AutomationFactory.CreateObject("WScript.Shell"))
{
string dotNetRoot =
wScript.RegRead(@"HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\InstallRoot");
}
4. Run another local application
using (dynamic wScript = AutomationFactory.CreateObject("WScript.Shell"))
{
//Refer WScript.Run at: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/d5fk67ky(v=VS.85).aspx
wScript.Run("iexplore http://wayneye.com", 1, true);
}
Note 1: WScript.Shell.Run method can accepts not only executable files, but also accepts *.bat, Windows Script Host files (*.vbs, *.js) or PowerShell script files, etc.
Note 2: Intention to elevate more permission by running another exe or script file definitely won’t success, for example, if I try to invoke AccessKHLM.js below from my OOB application I will get a 80070005 error code that indicates access denied:
var WshShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell");
WshShell.RegWrite("HKLM\\Software\\WayneTestValue\\", 1, "REG_BINARY");
WshShell.Close();

If you double click the Demo.js you will success since you are a Windows Administrator, while “Silverlight-based applications run in partial trust, which means they run within a security sandbox“, for more information please refer Trusted Application.
5. Phonate a sentence
using (dynamic speechApi = AutomationFactory.CreateObject("Sapi.SpVoice"))
{
speechApi.Speak(this.txtPhonateSource.Text);
}
6. Code to implement close button “X” appear on the upper-top corner.
using (var wScript = AutomationFactory.CreateObject("WScript.Shell"))
{
wScript.Run(@"cmd /k taskkill /IM sllauncher.exe & exit", 0);
}
This is a little bit tricky, I searched a while on google and found a great article Programmatically exit Silverlight 4 Out-of-browser application. Essentially the code invokes WScript.Shell and runs cmd and terminate sllauncher.exe, so that our OOB process got killed .
.
Conclusion
With elevated trust for Silverlight OOB applications, we can do much more than ever, it give more confidence to develope Enterprise business applications using Silverlight technology, yesterday I saw Scott Guthrie posted a blog talking about Silverlight, he mentioned Microsoft will absolutely continue work hard on Silverlight for Enterprise Businees Applications (both online and OOB).
Source Code Download
Silverlight4ManipulateSystem.zip
References
How to: Configure an Application for Out-of-Browser Support
http://http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd833073(v=VS.95).aspx
How to Configure your Silverlight App to run in Elevated Trust Mode
http://blogs.silverlight.net/blogs/msnow/archive/2010/04/20/tip-of-the-day-112-how-to-configure-your-silverlight-app-to-run-in-elevated-trust-mode.aspx
Silverlight Tip of the Day #19: Using Isolated Storage
http://blogs.silverlight.net/blogs/msnow/archive/2008/07/16/tip-of-the-day-19-using-isolated-storage.aspx
File Explorer using Silverlight 4 COM Interoperability
http://www.codeproject.com/KB/silverlight/FileExplorerInSilverlight.aspx
WshShell Object
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aew9yb99(v=VS.85).aspx